行业动态
缺氧肾脏损伤研究
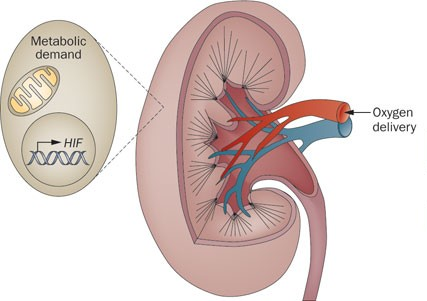
实验研究
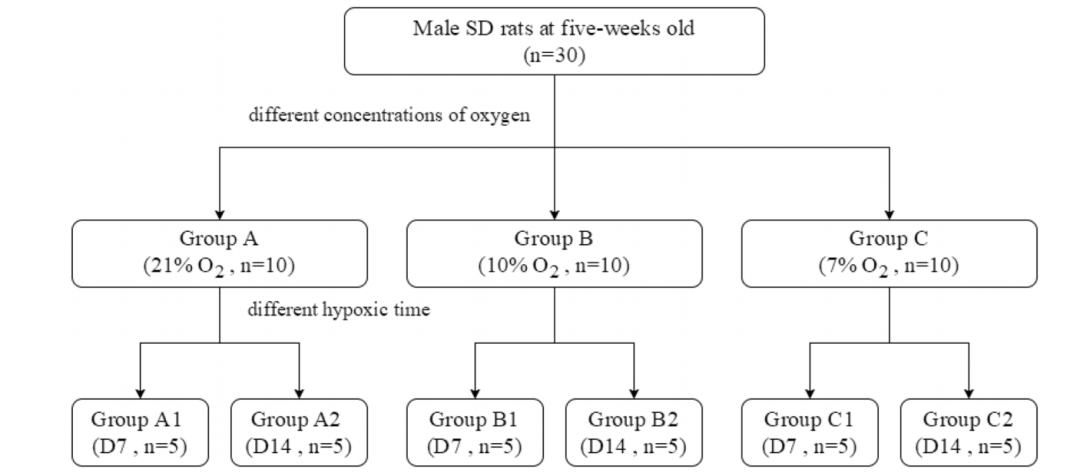
研究采用30只5周龄SD大鼠,进行不同条件的缺氧造模。
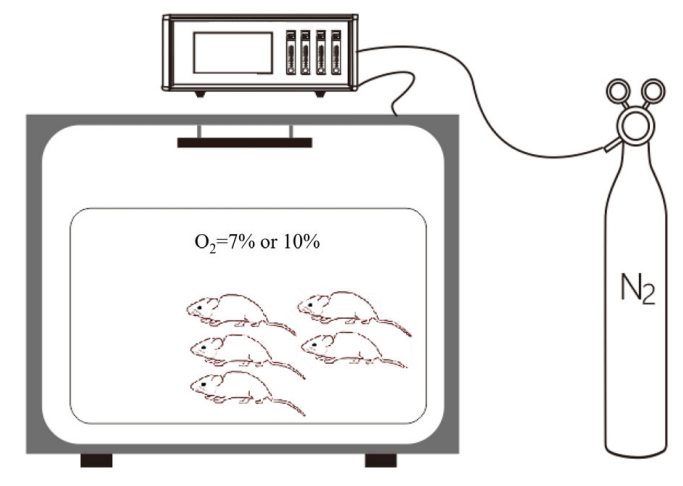
传统上,对于慢性缺氧模型,大鼠接受2周缺氧(10% O2)。氧合目标(Pa O2 90-60mmHg)是通过调整吸气氧气的分数(Fi O2)来实现的,对于高生存率和低PaO2水平,研究人员在研究中测量的最小O2浓度为7% O2。老鼠随机分布成三组根据吸入不同浓度的氧气(每组包括10只动物):21% O2在B组,10% O2和7% O2组每组进一步分为两个子组根据缺氧时间(1或2周)(图1)
*如上图,塔望科技可提供
低氧结束,大鼠注射麻醉。麻醉后,将大鼠仰卧位,固定在手术台上。采用腹侧中线切口隔离腹主动脉,将聚乙烯导管插入腹主动脉,并连接压力传感器进行数据采集血压测量系统。通过腹主动脉测量血压,并采血进行检测。

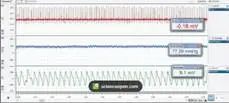
*如上图,塔望科技可提供
然后对这些大鼠进行放血安乐死。切除双肾进行分析。其中一个标本被闪存冷冻,立即保存在液氮容器中进行免疫印迹分析,而另一个样品在4%多聚甲醛溶液中浸泡进行纤维固定,然后进行染色和免疫组化检查。在尼康EclipseE600显微镜下观察组织切片,并使用尼康DS-Ri1数码相机拍摄不重叠的图像。
部分结果如下:
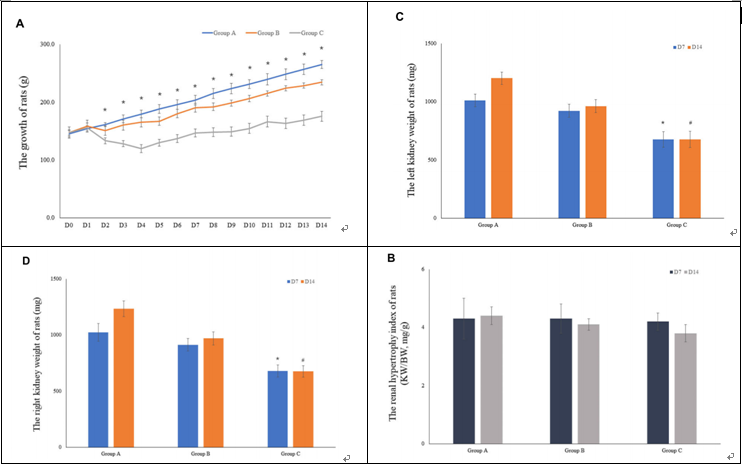
FIGURE 3 | The growth of rats and the weight of rat kidneys. (A) The mean body weight of the rats was determined on a daily basis for 14 consecutive days (10 rats were included in the analysis for the fifirst 7 days, and 5 rats were included for the remaining 7 days). (B) The renal hypertrophy index of rats on D7 (n = 5) and D14 (n = 5). (C) The mean left kidney weight of the rats was determined on D7 (n = 5) and D14 (n = 5). (D) The mean left kidney weight of the rats was measured on D7 (n = 5) and D14 (n = 5).
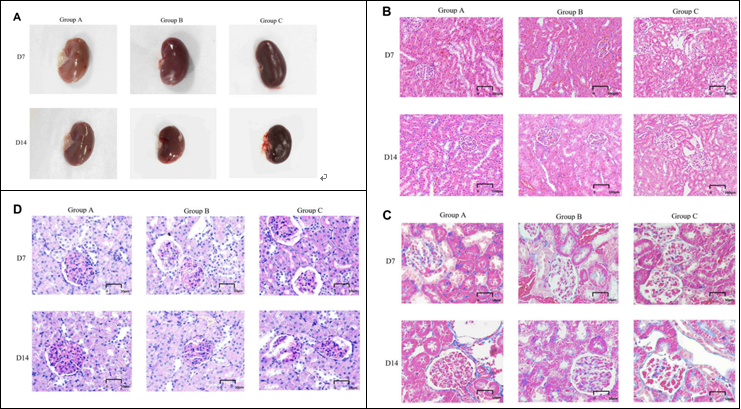
FIGURE 4 | General features and morphological traits in renal tissues obtained from animals subjected to normoxic and hypoxic conditions. (A) Gross view of a kidney. (B) A histological section of kidney tissue. The histological examination was performed at 20 × magnifification (scale bar = 100 µm).
(C) Periodic acid-Schiff staining (40 × magnifification, scale bar = 50 µm).
(D) Masson’s trichrome staining (40× magnifification, scale bar = 50 µm).
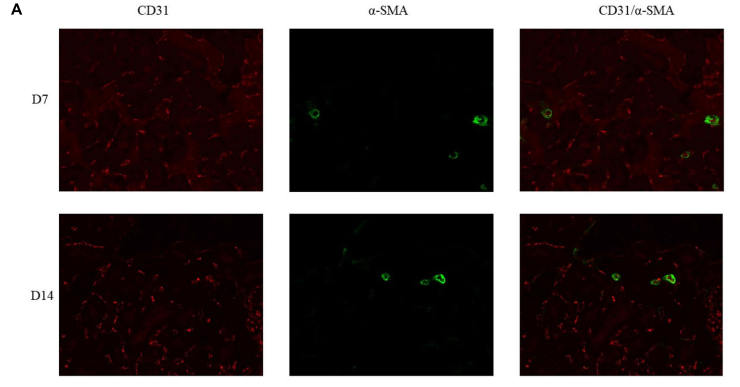
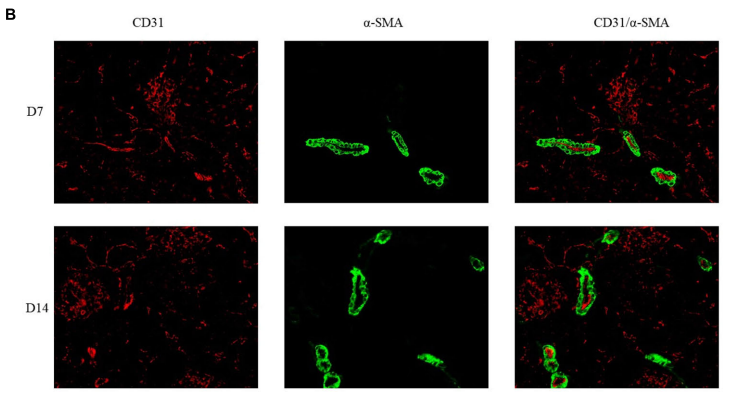
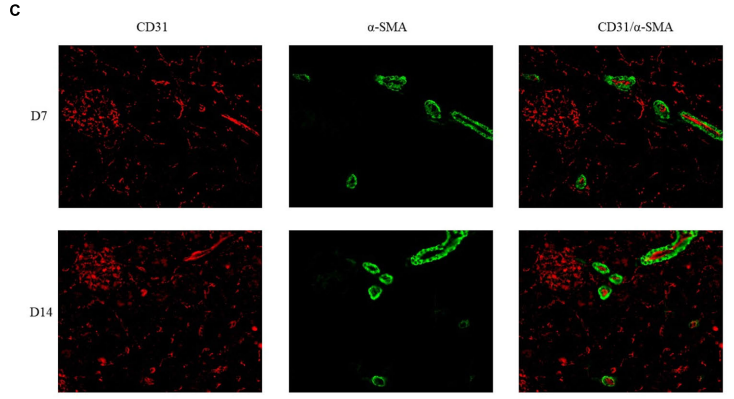
FIGURE 7 | Double immunoflfluorescence labeling of CD31 (red) and α-SMA (green) in rat kidneys; nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). (A) Mature blood vessel
density of rats in the 21% O2 group. (B) Mature blood vessel density of rats in the 10% O2 group. (C) Mature blood vessel density of rats in the 7% O2 group.
Original magnifification: ×400
